In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), one technology stands out as a game-changer: neural networks. These computational systems, inspired by the human brain’s structure and functionality, have ushered in a new era of machine learning and are transforming industries across the board. In this article, we will delve into the world of neural networks, exploring what they are, how they work, and their far-reaching impact on our lives.
Understanding Neural Networks
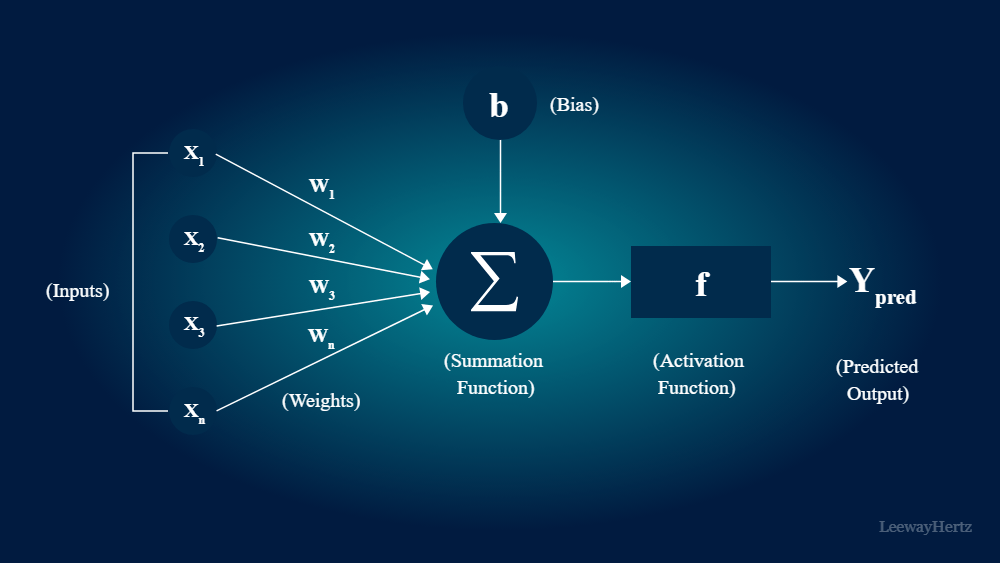
At its core, a neural network is a computational model that processes information much like the human brain. It is composed of interconnected units, or “neurons,” organized into layers. These neurons communicate with each other through weighted connections, and the strength of these connections is adjusted during the training process to learn from data.
The basic building blocks of a neural network are as follows:
- Input Layer: This is where data is introduced into the network. Each neuron in the input layer represents a feature or attribute of the data.
- Hidden Layers: These are intermediate layers between the input and output layers. They perform complex calculations to transform the input data into meaningful information.
- Output Layer: This layer produces the final result or prediction based on the input data and the network’s learned parameters.
The strength of neural networks lies in their ability to automatically learn and adapt to complex patterns in data, making them suitable for a wide range of tasks, from image recognition to natural language processing.
How Neural Networks Work
Neural networks work through a process called “forward propagation.” During this process, data is fed into the input layer, and it travels through the hidden layers, with each neuron performing a mathematical operation and passing its result to the next layer. This process continues until the data reaches the output layer, where a prediction or classification is made.
The real magic of neural networks, however, lies in “backpropagation.” This is the training phase where the network learns from its mistakes. It compares its predictions to the actual outcomes and adjusts the weights of its connections accordingly, minimizing the error. This iterative process is repeated many times until the network achieves a high level of accuracy.
Applications of Neural Networks
The versatility of neural networks is evident in their widespread applications. Here are some areas where they are making a significant impact:
- Image Recognition: Neural networks have revolutionized image recognition technology. They can identify objects, faces, and even diagnose medical conditions by analyzing images with incredible accuracy.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP tasks like language translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbots have greatly benefited from neural networks. They enable machines to understand and generate human language.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on neural networks to process sensor data and make real-time decisions, ensuring safe navigation on roads.
- Financial Forecasting: Neural networks are used for predicting stock prices, detecting fraudulent transactions, and optimizing investment strategies.
- Healthcare: In medicine, neural networks assist in disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient data.
- Gaming: Game developers employ neural networks to create intelligent non-player characters (NPCs) and enhance the gaming experience through adaptive gameplay.
- Recommendation Systems: Leading online platforms, such as Netflix and Amazon, employ neural networks to suggest products or content based on user preferences and behavior.
Challenges and Future Directions
While neural networks have achieved remarkable successes, they are not without challenges. These include the need for large amounts of labeled data, the risk of overfitting, and the “black box” nature of deep neural networks, making it difficult to interpret their decisions.
Looking ahead, researchers are actively working on addressing these challenges and exploring new frontiers. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques aim to make neural networks more transparent and interpretable, making them more trustworthy in critical applications. Additionally, advances in unsupervised and reinforcement learning are expanding the capabilities of neural networks and reducing their reliance on labeled data.
In conclusion, neural networks have emerged as a transformative force in the field of artificial intelligence. Their ability to learn from data and make complex decisions has led to breakthroughs in a wide range of industries. As research and development in neural networks continue to advance, we can expect even greater innovations that will shape the future of AI and how it impacts our lives. Whether it’s self-driving cars, personalized healthcare, or smarter recommendation systems, neural networks are at the heart of the AI revolution, propelling us into a future filled with intelligent machines.